The world of solar energy can feel like a maze of technical jargon. If you’ve ever scratched your head at terms like photovoltaic, inverter, or solar array, you’re not alone! Understanding solar terminology is key to making informed decisions about renewable energy. Let’s break it down in simple terms so you can navigate the solar landscape with confidence.
Solar Panels (Photovoltaic Panels)
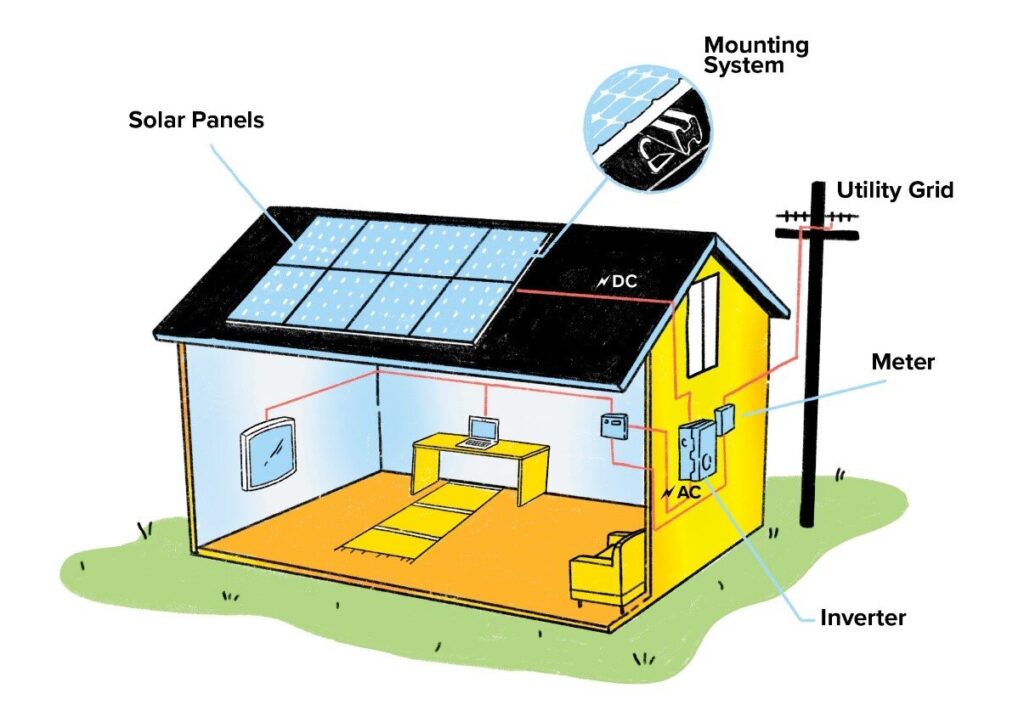
When people talk about solar energy, they’re usually referring to photovoltaic (PV) panels. Solar cells in these panels use sunlight to generate power. Each panel is made up of silicon-based cells that generate direct current (DC) electricity when exposed to sunlight.
Curious about how PV panels work? Check out our blog How Photovoltaic Panels Convert Sunlight into Energy.
Solar Array
A solar array is simply a group of solar panels connected to generate more electricity. Whether for a home or a large-scale solar farm, multiple panels are combined to meet specific energy needs. The more panels, the greater the energy output!
Inverter: The Brain of the System
Solar panels generate DC electricity, but our homes and appliances use alternating current (AC) electricity. That’s where the inverter comes in—it converts DC to AC, making the electricity usable.
There are different types of inverters:
- String Inverter: Connects multiple panels and converts electricity for the entire system.
- Microinverter: Installed on individual panels, allowing for optimized performance.
- Hybrid Inverter: Works with both solar panels and battery storage for greater energy efficiency.
Net Metering
This term is very famous in Pakistan for all the good reasons. Why? I’ll tell you why: if your solar panels produce more electricity than you use, net metering allows you to send excess energy back to the grid in exchange for credits on your electricity bill. This means you can offset your power costs when your system isn’t generating electricity (like at night).
Want to learn more? Read our detailed guide on Solar Energy Billing Explained: Net Metering vs. Feed-in Tariffs.
Solar Battery Storage
What happens when the sun isn’t shining? That’s where solar batteries come in. These batteries store excess solar energy, so you can use it when your panels aren’t generating power. Popular options include lithium-ion batteries, which offer high efficiency and long lifespan.
Solar Efficiency & Performance Ratio
Solar Efficiency: This refers to how well a solar panel converts sunlight into electricity. Most residential panels have an efficiency rate of 15-22%.
Performance Ratio (PR): PR measures the actual energy output compared to the theoretical maximum. A higher PR means a better-performing system!
Solar Charge Controller
A solar charge controller manages the energy flowing from solar panels to batteries, preventing overcharging and improving battery lifespan. It’s a crucial component for off-grid and hybrid solar systems.
Grid-Tied vs. Off-Grid Solar Systems
- Grid-Tied: Connected to the electricity grid, allowing users to benefit from net metering.
- Off-Grid: Independent systems relying on solar panels and battery storage, ideal for remote locations.
- Hybrid Systems: Combine solar panels, batteries, and grid connection for maximum flexibility.
Final Thoughts
Understanding solar terminology empowers you to make informed decisions about renewable energy. Whether you’re exploring solar for your home or business, knowing the basics—from photovoltaics to inverters—helps you navigate the transition to clean energy with confidence.
So, Solar Terminology is explained to you, now are you ready to switch to solar? Together, let’s utilize the sun’s power!







