
Why do these trends matter now? Solar technology is changing faster than most people realize. For homeowners, businesses, and developers in Pakistan, these changes affect system sizing, payback, rooftop decisions, and even regulatory planning. I’ll walk you through the most important solar panel technology trends, show data-backed impacts, and explain what they mean for buying, installing, or designing solar systems here. I’ll also link practical examples to our previous coverage on home automation and policy.
1. Tandem & Perovskite Cells — big efficiency gains on the horizon

Tandem cells combine silicon with another absorber (most often perovskite) to exceed silicon’s single-junction limits. Industry R&D and recent lab-to-pilot milestones suggest commercial tandem modules are moving quickly toward market-ready status. These cells promise meaningful jumps in module efficiency — potentially shaving system area or boosting kWh produced per rooftop. Globally, research efficiency records keep rising, and companies are pushing commercialization efforts.
What this means for Pakistan: Higher-efficiency modules mean more generation from constrained rooftops or less land required for utility projects — useful for dense housing and urban solar rollout.
2. TOPCon, HJT, and incremental cell tech — steady efficiency and lower LCOE
While tandems get headlines, incremental silicon improvements like TOPCon and heterojunction (HJT) dominate manufacturing today and push module efficiencies up while lowering costs per watt. Industry surveys show a rising share of TOPCon in global shipments — a mature path to better-performance modules without radically changing manufacturing.
Quick example: If a TOPCon module improves nameplate output by 5% over an older panel, a 5-kW system’s annual yield rises measurably — shortening payback and improving ROI.
3. Bifacial modules + single-axis trackers — additive gains at utility scale

Bifacial modules capture light from both faces; when combined with single-axis trackers that follow the sun, the system yields an increase. Recent industry reports show tracker boosts of ~15–20% and bifacial gains of 2–10%, and these gains are additive — making bifacial + trackers the cost-effective baseline for many large projects.
Simple math: A fixed array that produces 1,000 kWh/year could produce ~1,150–1,300 kWh/year with tracking + bifacial gains in many locations — a 15–30% increase in revenue per installed MW.
4. Integration with storage: batteries are table stakes, not extras
The economics of solar plus storage have shifted. Lithium-ion (especially LFP) battery costs dropped and performance improved — making hybrid systems practical for homes and businesses. Storage enables self-consumption, peak-shaving, and firming of intermittent PV. Policy and grid rules that reward flexibility make storage even more attractive. Grid-interactive inverters allow solar systems to provide dispatchable services to the grid.
Pakistan angle: With frequent load-shedding and high night tariffs, adding storage increases resilience and may improve overall ROI despite higher initial cost.
5. Smart inverters, controls, and AI — squeezing more energy out of each panel
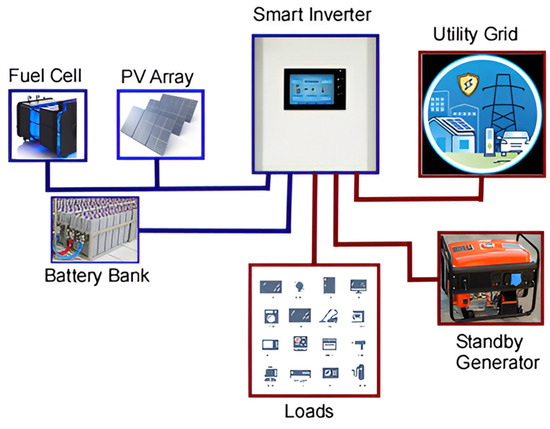
Smart inverters, ML-driven monitoring, and predictive maintenance are becoming standard. These systems detect shading, degradation patterns, and soiling, and they optimize panel-level performance and system-level dispatch. Large fleets of distributed PV can be controlled like virtual power plants, helping grids manage variability. Think of AI as your operations manager — spotting small faults before they become big losses.
6. Thin-film, flexible PV and BIPV — new form factors for urban Pakistan

Ultra-thin and flexible PV (including some perovskite-based approaches) opens new installations: curved roofs, facades, and building-integrated photovoltaics (BIPV). Governments investing in building retrofits and architects seeking low-profile aesthetics will find these panels valuable. Japan and other countries are investing heavily to industrialize flexible cells — that momentum matters globally.
Use case: Small BIPV installations on commercial buildings reduce dependence on rooftop space while improving building value and appearance.
7. Circularity, recycling, and supply-chain resilience

As PV deployment scales, end-of-life management and responsible sourcing become central. Recycling modules and recovering silver, silicon, and other materials lowers embodied carbon and secures supply chains. The industry is moving toward better take-back schemes and modular designs for easier recycling — a theme investors and policymakers now prioritize.
8. Agrivoltaics & floating PV — dual-use land solutions
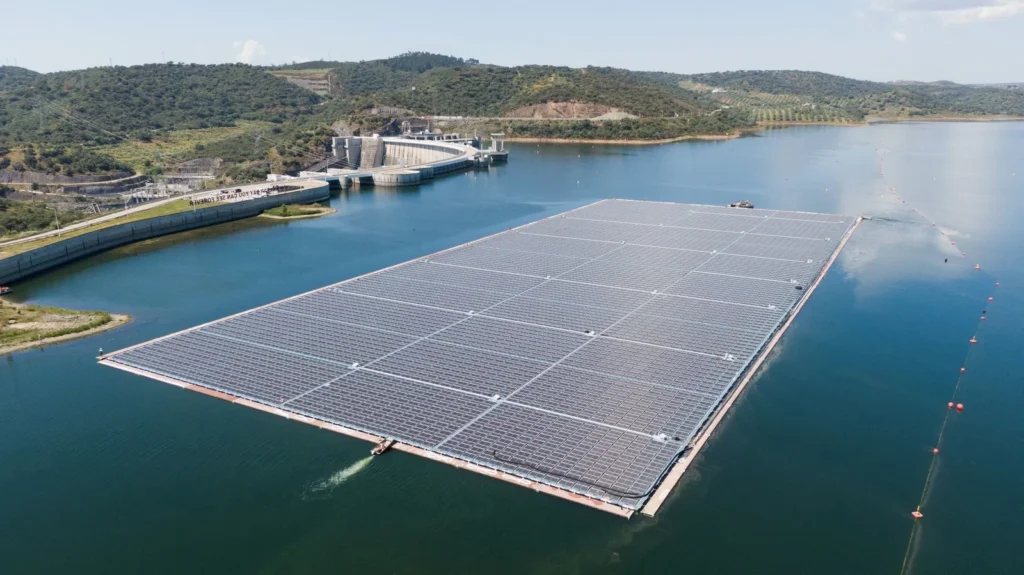

Agrivoltaics (growing crops under panels) and floating solar (over reservoirs) are gaining traction because they reduce land-use conflicts and improve water management. Floating PV also benefits from cooling effects that improve performance. For Pakistan — with competing demands on agricultural land — agrivoltaics offer a way to add clean power without sacrificing farmland.
Market snapshot: scale, shipments, and who’s leading
Global PV shipments and module manufacturing remain dominated by China, but manufacturing diversification is beginning. Recent market updates show a large increase in global PV shipments and a continued decline in module prices, while TOPCon and bifacial technologies make up a growing share of production. These shifts mean lower upfront costs and better-performing modules for developers worldwide.
What this means for Pakistani buyers & installers
- Rooftop buyers: Higher-efficiency panels (TOPCon, HJT, eventual tandems) mean more kWh per square meter — good for limited-roof space. Consider panel efficiency and temperature coefficients when comparing quotes.
- Commercial & utility developers: Bifacial + trackers are increasingly the lowest-cost option per kWh. Floating PV and agrivoltaics are promising where land is scarce.
- System designers: Add storage and smart inverters to capture arbitrage and grid services — this can materially improve revenue and resilience.
- Installers & policymakers: Plan for recycling and end-of-life management now to avoid regulatory headaches later.
Short example calculation: tracker + bifacial lift

- Fixed array annual yield = 1,000 kWh/MW installed (baseline for simplicity).
- Add single-axis tracking = +18% → 1,180 kWh.
- Add bifacial effective gain = +6% → 1,251 kWh.
That’s a 25.1% increase in energy yield for modest incremental cost — a meaningful difference in payback.
(Percent figures drawn from industry analyses and tracking/bifacial reports.)
How JS Technology helps you benefit from these trends
- We size systems using modern module types (TOPCon, bifacial) and run yield modeling that accounts for temperature, soiling, and local irradiance.
- For commercial projects, we model tracker + bifacial scenarios to show true LCOE.
- We offer hybrid solar+storage packages and smart inverters for resilience and revenue stacking.
- We advise on future-proof procurement (warranties, recycling pathways) so your investment retains value.
Conclusion — The horizon is nearer than you think
Solar panel technology trends are not one leap; it’s many steady advances that together change the economics and practicality of clean power. For Pakistan, that means more kilowatts per rooftop, smarter systems that lower bills, and utility options that use land more efficiently. If you’re planning a solar installation today, factor in high-efficiency modules, storage, smart controls, and a plan for end-of-life recycling. Those choices are the difference between a system that’s good today and one that still pays off a decade from now.
Want a practical roadmap for your rooftop or site? Let’s run the numbers together and design a system that uses the best of these emerging trends.
Further reading & sources (key references used above): IEA PVPS Trends 2024; NREL PV efficiency resources; PV Magazine reporting on bifacial + trackers; industry reviews on perovskite commercialization.
FAQs
Q1: When will perovskite tandem panels be available commercially?
A: Pilot deployments and limited commercial modules are appearing; broad mainstream adoption depends on stability and scale-up over the next few years.
Q2: Are bifacial panels worth it for rooftop systems?
A: Bifacial panels are most effective where rear irradiance (ground albedo) and installation height allow rear-side harvest—utility and ground-mounted systems benefit more than tightly-packed urban rooftops.
Q3: How much do trackers increase output?
A: Typical single-axis tracker gains are around 15–20% compared to fixed tilt; combined with bifacial gains, this can be additive.
Q4: Should I add batteries now or later?
A: Storage improves resilience and can increase ROI in high-tariff or unstable-grid markets. Consider staged deployment if upfront cost is a concern.
Q5: Will new tech raise the cost of maintenance?
A: New module types need standard maintenance; smart monitoring reduces downtime and helps prioritize maintenance, often lowering life-cycle costs.
Expert signals & credible sources
- IEA and PVPS trend reports track deployment patterns and note how cell and module tech are evolving. IEA-PVPS+1
- NREL maintains the authoritative efficiency records that show where research is pushing cell performance. NREL
- Industry reporting highlights commercialization pushes for perovskite tandems and practical bifacial+tracker wins. RSC Publishing+1
(These are the most load-bearing sources supporting the trends above.)







